Images
Other useful flags to attach to the ‘docker run’ command are:-d — Detach container on start-rm — Remove container once it stops-p — Publish host IP and host port to the container port (e.g. Docker run hostip:hostport:containerport)-v — Define volume mounts to share storage volume across containers. Docker is fantastic tool for building out your infrastructure, however it does have a fairly steep learning curve. That’s why I created this Docker Cheat Sheet.I was constantly looking up what docker commands I needed to run to build an image from a dockerfile, run a container, mount a volume, etc.
Building images
Use a different Dockerfile:
Skipping cache:
Prune images
Delete all images without an associated container:
Inspect images
In order to inspect the images, you may run them as container with a shell command - usually bash but sh for Alpine based ones:
Containers
Run from image
Explanation:
detached
image tag
name of the container (optional)
You can instruct Docker to automatically remove the container when it is terminatedby adding the --rm flag:
Please note that this also removes the logs for the container.
Environment variables can be passed to the container with the --env flag:
Remove and prune
Remove container
Please note that the corresponding image isn't affected.
Prune containers
Remove all stopped containers:
Remove all stopped containers older than a day:
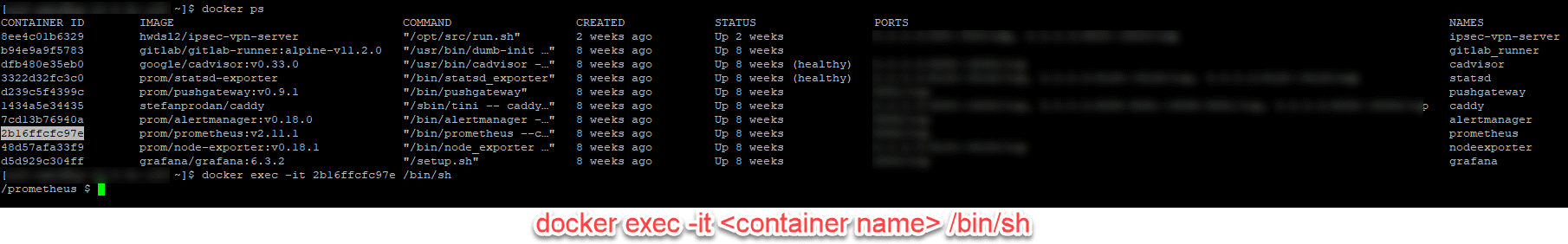
Shell on a running container
You can also pass environment variables to the command executed in the Docker container:
Note: the flags for the environment preceed the flag for the container.
Copy files from/to container
From:
To:
Logs
To see the log messages for the container nginx:
However, this shows only the messages without any further information.
You can add the timestamp with the --timestamps commandline option:
Container Information
IP address
To get the IP address of the container perldancer:
Determine whether a container is running properly
This checks whether the container with the name sympa is active and running, e.g. not restarting because of a problem with the command it executes on startup.

Startup problems
Missing environment variables, e.g.
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORDfor mysql container
Compose
Run containers and detach:
Base commands:
Creating a new container
Create container and run command:
To get a bash to see what's inside container (good alternative to docker attach)
Kill container
Kill all containers
Remove image from the local system
May be useful:
Get IP Address of Host
Docker registry related commands:
Docker Stack (compose file v3)
Volumes
Volumes in Docker can be used for persistent data. If we remove the MySQL container, we will lose all the data we put into our blog.To avoid this situation, we can create a Docker volume and mount it in /var/lib/mysql of the database container. The life of this volume would be totally separate from the container lifecycle.
Compose can help us with managing these so-called named volumes. They need to be defined under the volumes key in a Compose file and can be used in a service definition. Below is a snippet of our modified Compose file, which creates a mysql named volume and uses it in the mysql service.
Compose will automatically create this named volume, and you will be able to see it with the docker volume ls command as well as find its path with docker volume inspect <volume_name>. Here is an example:
Docker Run Flags Cheat Sheet Pdf
Be careful, however. If you bring down the application with docker-compose down, the persistent volume will be deleted and you will lose your data.
Running on Linux
Installation guide: https://docs.docker.com/engine/installation/linux/ubuntulinux/Compose installation: https://docs.docker.com/compose/install/
- I had some permissions problem on EC2. Had to dissect the URL and instead of curl use wget. Then rename the downloaded file to
docker-composeand move it tomv ./docker-compose /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
Start the Docker Daemon
If you get the error: ERROR: Couldn't connect to Docker daemon at http+docker://localunixsocket - is it running? you might have to use commands with sudo: sudo docker-compose up
Docker Command Line Cheat Sheet
Create new container
a) docker run -i -t ubuntu /bin/bashb) docker run --name rails_dev_container -i -t ubuntu ubuntu /bin/bashThe command line flags - i -t provide an interactive shell in the new containerShow running docker containers > docker ps
Show list of current containers >a) docker ps -a (Show all containers, both stopped and running)b) docker ps -n x (shows the last x containers, running or stopped, ex: docker ps -n 5)
Show last container that was run (whether is is running or stopped) > docker ps -l
List docker images > docker images
Delete a container
a) docker rm <container_id> (ex: docker rm aa3f365f0f4e)b) docker rm <container_name> (ex: docker rm rails_dev_container)Delete all containers > docker rm $(docker ps -a -q)
Delete an image > docker rmi <image_id>
Delete all images > docker rmi $(docker images -q)
Start a stopped containera) docker start <container_id> (ex: docker start aa3f365f0f4e)b) docker start <container_name> (ex: docker start rails_dev_container)
Attach to a containera) docker attach <container_id> (ex: docker attach aa3f365f0f4e)b) docker attach <container_name> (ex: docker attach rails_dev_container)
Creating daemonized containersdocker run --name daemon_container -d ubuntu /bin/sh -c 'while true; do echo hello world; sleep 1; done'(-d flag detachs the container to the background)
Docker Cheat Sheet 2020
To see what's happening inside the containerdocker logs rails_dev_containerdocker logs -f rails_dev_container (like the tail -f)docker logs -ft rails_dev_container (prefix log entries with timestamps)docker logs --tail 10 daemon_container (get the last 10 lines of the log)docker logs --tail 0 -f daemon_container (follow the logs without having to read the whole log file)
Inspecting the container's processesdocker top daemon_container
Running a process inside a containera) Backgrounddocker exec -d daemon_container touch /etc/new_config_fileb) Interactivedocker exec -t -i daemon_container /bin/bash
Stopping a daemonized containerdocker stop daemon_containerordocker stop aa3f365f0f4e
Automatic container restartsdocker run --restart=always --name daemon_container -d ubuntu /bin/sh -c 'while true; do echo hello world; sleep 1; done'(docker will try to restart the container no matter what exit code is returned)--restart=on-failure:5 (this will attempt to restart the container a maximum of 5 times if a non-zero exit code is received)
Finding more about our containerdocker inspect daemon_containerdocker inspect --format='{{ .State.Running }}' daemon_containerdocker inspect --format '{{ .HostnamePath }}' daemon_containerdocker inspect --format '{{ .Name }} {{ .HostnamePath }}' daemon_containerlist multiple containersdocker inspect --format '{{ .Name }} {{ .HostnamePath }}' daemon_container dameon_cont_2
Pulling imagesdocker pull ubuntudocker pull fedoradocker pull fedora:21docker pull jamtur01/puppetmaster
Searching for imagesdocker search puppet
Sign into the Docker Hubdocker login
Using Docker commit to create imagesCreate a container from the ubuntu imagedocker run -i -t ubuntu /bin/bashInstall Apache into the containerapt-get -yqq updateapt-get -y install apache2exit from the containerdocker commit 6b84282435f8 dvdoc/apache2ordocker commit -m='A new custom image' --author='DV Suresh'
6b84282435f8 dvdoc/apache2:webserver
